Special Services
Bio Medical Waste Management
The Bio-medical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 1998 and further amendments were passed for the regulation of bio-medical waste management. On 28 th Mar 2016 Biomedical Waste Management Rules 2016 were also notified by Central Govt. Each state’s Pollution Control Board or Pollution control Committee will be responsible for implementing the new legislation.[15]
In India, though there are a number of different disposal methods, the situation is desultory and most are harmful rather than helpful. If body fluids are present, the material needs to be incinerated or put into an autoclave. Although this is the proper method, most medical facilities fail to follow the regulations. It is often found that biomedical waste is dumped into the ocean, where it eventually washes up on shore, or in landfills due to improper sorting or negligence when in the medical facility. Improper disposal can lead to many diseases in animals as well as humans. For example, animals, such as cows in Pondicherry, India, are consuming the infected waste and eventually, these infections can be transported to humans who consume their meat or milk. Large number of unregistered clinics and institutions also generate bio-medical waste which is not controlled.
Due to the competition to improve quality and so as to get accreditation from agencies like ISO, NABH, JCI, many private organizations have initiated proper bio-medical waste disposal but still the gap is huge.
The latest guidelines for segregation of bio-medical waste recommend the following color coding – [16]
- Red Bag – Syringes (without needles), soiled gloves, catheters, IV tubes etc. should be all disposed of in a red colored bag, which will later be incinerated.
- Yellow Bag – All dressings, bandages and cotton swabs with body fluids, blood bags, human anatomical waste, body parts are to be discarded in yellow bags.
- Cardboard box with blue marking – Glass vials, ampules, other glass ware is to be discarded in a cardboard box with a blue marking/sticker.
- White Puncture Proof Container (PPC) – Needles, sharps, blades are disposed of in a white translucent puncture proof container.
- Black Bags – These are to be used for non-bio-medical waste. In a hospital setup, this includes stationary, vegetable and fruit peels, leftovers, packaging including that from medicines, disposable caps, disposable masks, disposable shoe-covers, disposable tea cups, cartons, sweeping dust, kitchen waste etc.
FORM - 1 [Accident Reporting] &
FORM - IV [Annuval Report]
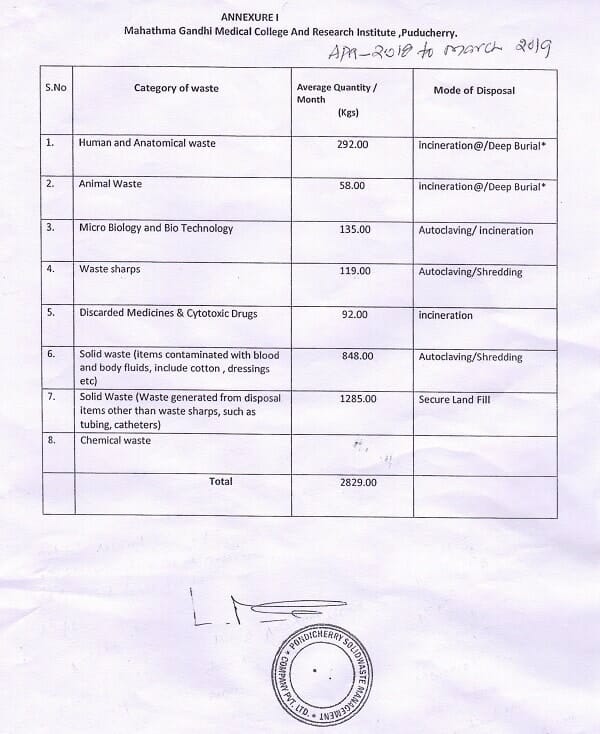
Annexure I
Mahathma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Puducherry. (April 2018 to March 2019)